主要内容 #
1. 特征 #
假如有这样的一批数据需要定义
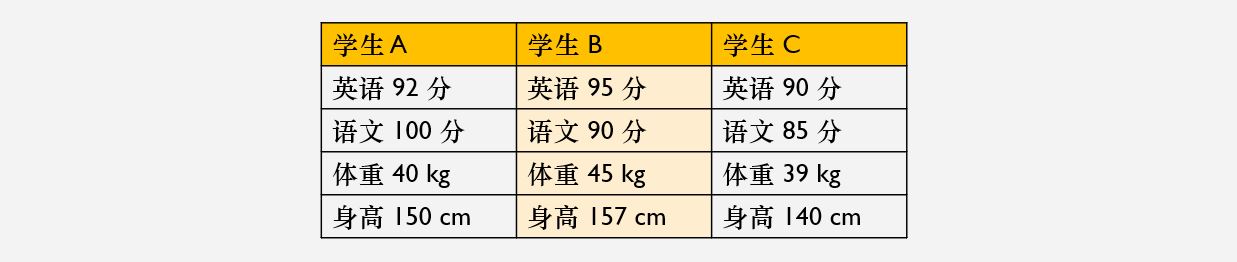
则我们需要这样来写
int student_A_English = 92; int student_A_Chinese = 100; int student_A_Weight = 40; int student_A_Height = 150; int student_B_English = 95; int student_B_Chinese = 90; int student_B_Weight = 45; int student_B_Height = 157; int student_C_English = 90; int student_C_Chinese = 85; int student_C_Weight = 39; int student_C_Height = 140;
这么写,很显然非常繁琐。C++ 有一种专门针对此类数据的做法。
请先分析,上述的数据是否可以分成三组?分组后,每一组需要设置那些变量?
2. 结构体 #
简单来说,我们可以将数据分为三组,而每组的情况如下:
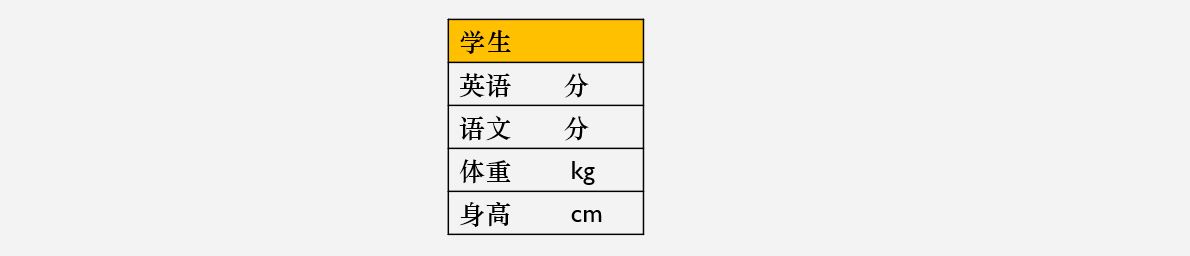
定义 #
这样,每组可以设置 4 个变量。上图的形式,可以写作如下:

// 定义结构体
struct student
{
int English;
int Chinese;
int Weight;
int Height;
};
// 定义变量
student dashima_A;
dashima_A.English = 92;
dashima_A.Chinese = 100;
dashima_A.Weight = 40;
dashima_A.Height = 150;
输入输出举例 #
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
// 定义结构体
struct student
{
int English;
int Chinese;
int Weight;
int Height;
};
int main()
{
// 定义变量
student dashima_A;
dashima_A.English = 92;
dashima_A.Chinese = 100;
dashima_A.Weight = 40;
dashima_A.Height = 150;
cin >> dashima_A.Chinese;
cout << dashima_A.English << endl;
return 0;
}
3. 构造函数 #
关于结构体,有一点不同的就是,结构体含有一个构造函数。什么叫构造函数呢?请看示例程序:
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
// 定义结构体
struct student
{
// 定义结构体的构造函数
student(int _English,
int _Chinese,
int _Weight,
int _Height)
{
m_English = _English;
m_Chinese = _Chinese;
m_Weight = _Weight;
m_Height = _Height;
}
int m_English;
int m_Chinese;
int m_Weight;
int m_Height;
};
int main()
{
// 定义变量
student dashima_A(92,100,40,150); // 构造函数,使变量赋值变得更加简洁。
//dashima_A.English = 92;
//dashima_A.Chinese = 100;
//dashima_A.Weight = 40;
//dashima_A.Height = 150;
student dashima_B(95,90,45,157);
student dashima_C(90,85,39,140);
cin >> dashima_A.Chinese;
cout << dashima_A.English << endl;
return 0;
}
习题 #